TACS Energy:
Smart Grid: Application of Big Data and Machine Learning in
Smart Grid and Associated Security Concerns: A Review
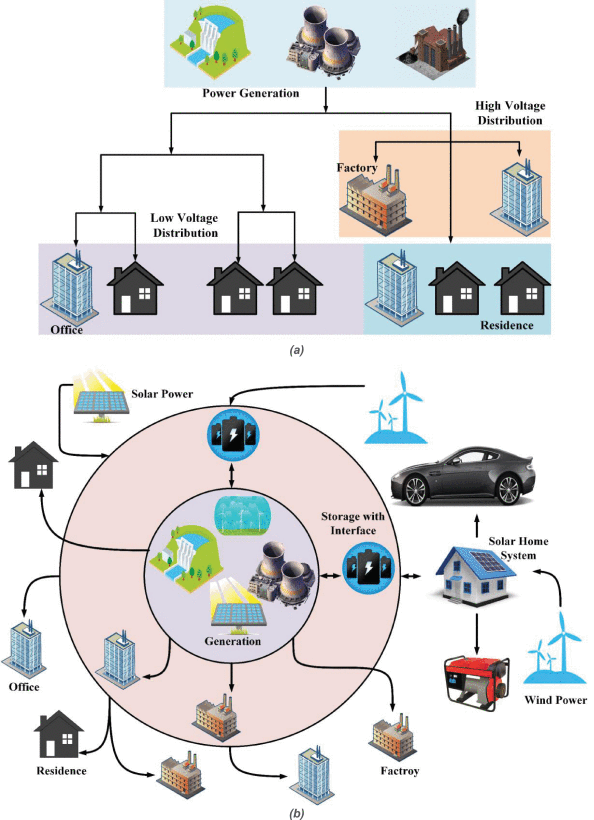
Utility grids: (a) conventional grid (b) smart grid. In the
conventional system power flows from in one direction only; but
for smart grid, there is no strict structure. Generation can
occur at the consumer side too, such as the wind and the solar
farms at the outer periphery of the topology. Power flow can
also be bidirectional, demonstrated by the energy storages and
the house in this illustration.
Application of Big Data and Machine Learning in
Smart Grid, and Associated Security Concerns: A Review
A comprehensive study is conducted on the
application of big data and machine learning in the electrical
power grid introduced through the emergence of the
next-generation power system-the smart grid (SG). Connectivity
lies at the core of this new grid infrastructure, which is
provided by the Internet of Things (IoT). This connectivity, and
constant communication required in this system, also introduced
a massive data volume that demands techniques far superior to
conventional methods for proper analysis and decision-making.
The IoT-integrated SG system can provide efficient load
forecasting and data acquisition technique along with
cost-effectiveness. Big data analysis and machine learning
techniques are essential to reaping these benefits. In the
complex connected system of SG, cyber security becomes a
critical issue; IoT devices and their data turning into major
targets of attacks. Such security concerns and their solutions
are also included. Key information obtained through literature
review is tabulated in the corresponding sections to provide a
clear synopsis; and the findings of this rigorous review are
listed to give a concise picture of this area of study and
promising future fields of academic and industrial research,
with current limitations with viable solutions along with their
effectiveness.
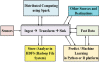
IoT
architecture. Data collected by sensors can be sent to
different systems which use various software platforms to carry
out
intended tasks.
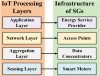
Structure for IoT implemented layers for SGs. Each IoT
layer corresponds to a certain layer of SG infrastructure.
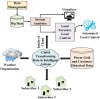
System architecture for load shedding and smart load
controlling algorithm. All the components of the system are
connected to the cloud which makes decisions based on the system
inputs, and sends out commands for execution. The directions of
the
arrows indicate the flow of data.
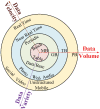
Big
data characteristics: large volume of data with lots of
variations which are generated, stored, or transmitted at a high
at a high velocity can be labeled as big data.
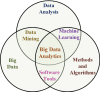
The
components that create big data analytics. Big data and the
techniques to analyze it has created the discipline of big data
analytics.
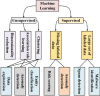
Application of machine learning in smart grid security.
Unsupervised and supervised – both approaches can be used to
carry out an array of tasks including threat identification and
data categorization.

Security concerns of IoT integrated SG system.
These
can be categorized into four major types: physical threat,
network threat, software threat, and encryption threat. The
security concerns under each type are marked in corresponding
color.
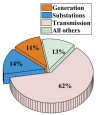
Attacks on major power grid components during 1994-2004;
the transmission system faced most of the attacks, reaching 62%.
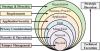
Layered security framework for smart grids.
This
comprehensive approach considers security at each stage of the
infrastructure, rather than only smart meter placed at consumer
location. Strategic direction and technical execution forms the
two major contributors in defining the framework
responsibilities.
Source
Application of Big Data and Machine Learning in Smart Grid and
Associated Security Concerns: A Review (pdf) -IEEE
|